Understanding the Importance of Brain Health in Nigeria
Brain health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being that affects every individual across their lifespan. It refers to the optimal functioning, resilience, and well-being of the brain. This concept goes beyond just avoiding diseases; it encompasses how well the brain supports daily life, thinking, emotions, and behaviors. Maintaining good brain health can reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke, while also enhancing quality of life emotionally, socially, and physically.
The American Heart Association/American Stroke Association defines brain health as the optimal capacity to function adaptively across various domains. These include attention, perception, learning, memory, communication, problem-solving, decision-making, mobility, and emotional regulation. Understanding these aspects helps individuals appreciate the significance of maintaining brain health throughout their lives.
Key Factors Influencing Brain Health in Nigerians
Nigerians need to be aware of the vital role that brain health plays in society. A healthy brain offers cognitive benefits such as improved memory, creativity, problem-solving, and clear thinking. It also provides emotional benefits like enhanced self-awareness and better emotional regulation, which contribute to a fulfilling life. Ultimately, optimal brain health has positive social and economic impacts that support overall well-being and societal progress.
Prioritizing brain health at every stage of life is essential because the brain influences daily activities. Various factors impact brain health in Nigeria, affecting individuals from infancy to adulthood. For instance, lack of access to prenatal care, poor maternal health, and inadequate nutrition affect infants’ brain development. The increasing use of illicit drugs and excessive alcohol consumption among young adults can negatively impact brain health, while cardiovascular risks like hypertension and diabetes in adults increase the likelihood of stroke.
Genetic predisposition, infections such as meningitis and malaria, malnutrition, and nutrient deficiencies also play significant roles. Insufficient sleep, limited healthcare access, and socio-economic challenges further hinder brain health. Cultural beliefs, violence, conflicts, and displacement can lead to traumatic brain injuries and mental health issues. Additionally, the emigration of skilled professionals strains the healthcare system, and environmental toxins like air and water pollution can impair brain function.
Strategies for Maintaining Brain Health
Individuals can promote brain health by engaging in regular physical activity, ensuring adequate sleep (6 to 8 hours), and consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats. Managing chronic medical conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity is also crucial. Nurturing social relationships, staying engaged with others, and managing stress are important steps. Committing to lifelong learning and participating in mentally stimulating activities can further enhance brain health.
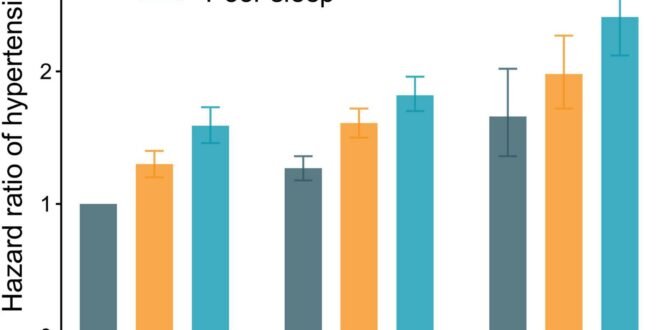
Hypertension and poor sleep quality or quantity have been linked to declines in brain health. Both conditions interact, as poor sleep can worsen blood pressure regulation, and hypertension can interfere with sleep quality. Chronic high blood pressure can damage the brain by reducing blood flow, leading to small vessel disease and an increased risk of stroke. Poor sleep impairs memory, cognitive function, and emotional regulation, while also disrupting the brain’s “clean-up” system.
Diet and Brain Health
A varied diet that includes different fruits, green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats is essential for brain health. While no single superfood guarantees brain health, consistency and variety are key. Combining a good diet with exercise, sleep, stress management, and learning yields the best results. Foods to avoid or limit include highly processed items, refined sugars, trans fats, and excessive alcohol, which can harm brain health over time.
Policies and Challenges in Supporting Brain Health
Currently, there are no specific policies in place to support brain health in Nigeria. However, the Mental Health Bill 2021, signed into law in 2023, addresses mental disorders, substance use, and community services, aiming to integrate mental health into primary healthcare. While this framework implicitly supports brain health through access to mental healthcare, it is distinct from brain health itself.
Challenges such as inadequate resources, insufficient infrastructure, a shortage of trained professionals, and socioeconomic factors like poverty and unemployment hinder the provision of services to support brain health. Cultural beliefs and a lack of awareness about brain health also contribute to these challenges.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Brain Health
Increasingly, many Nigerians are experiencing isolation, which can significantly impact brain health. Loneliness acts as a physiological and neurological stressor, reshaping brain function and structure. Social isolation leads to poor relationships, psychosocial stress, and long-term consequences such as depression and memory loss. Long-term loneliness increases the risk of dementia, Alzheimer’s, and cognitive impairment, independent of age or genetics.
Restoring Brain Health After Disruption
Yes, brain health can often be restored or significantly improved after disruption due to trauma, chronic stress, anxiety, or other psychological conditions. The brain’s adaptability, known as neuroplasticity, allows it to reorganize itself, form new neural connections, and compensate for damage. Recovery depends on factors such as the cause and extent of injury, the person’s age, overall health, support system, and access to appropriate treatment.
 Info Malang Raya Its All About World News
Info Malang Raya Its All About World News